TLS Protocol (HTTPS)
All 4D servers can communicate in secured mode through the TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol:
- the web server
- the application server (client-server desktop applications)
- the SQL server
Overview
The TLS protocol (successor of SSL) has been designed to secure data exchanges between two applications —mainly between a web server and a browser. This protocol is widely used and is compatible with most web browsers.
At the network level, the security protocol is inserted between the TCP/IP layer (low level) and the HTTP high level protocol. It has been designed mainly to work with HTTP.
Network configuration using TSL:
The TLS protocol is designed to authenticate the sender and receiver and to guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of the exchanged information:
- Authentication: The sender and receiver identities are confirmed.
- Confidentiality: The sent data is encrypted so that no third person can understand the message.
- Integrity: The received data has not been changed, by accident or malevolently.
TLS uses a public key encryption technique based on a pair of asymmetric keys for encryption and decryption: a public key and a private key. The private key is used to encrypt data. The sender (the website) does not give it to anyone. The public key is used to decrypt the information and is sent to the receivers (web browsers) through a certificate. When using TLS with the Internet, the certificate is delivered through a certification authority, such as Verisign®. The website pays the Certificate Authority to deliver a certificate which guaranties the server authentication and contains the public key allowing to exchange data in a secured mode.
For more information on the encryption method and the public and private key issues, refer to the
ENCRYPT BLOBcommand description.
Minimum version
By default, the minimum version of the secured protocol accepted by the server is TLS 1.2. You can modify this value by using the Min TLS version selector with the SET DATABASE PARAMETER command.
You can control the level of security of your web server by defining the minimum TLS version accepted for connections.
How to get a certificate?
A server working in secured mode means that you need a digital certificate from a certification authority. This certificate contains various information such as the site ID as well as the public key used to communicate with the server. This certificate is transmitted to the clients (e.g. Web browsers) connecting to this server. Once the certificate has been identified and accepted, the communication is made in secured mode.
Web browsers authorize only the certificates issued by a certification authority referenced in their properties.
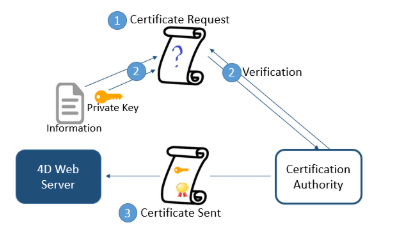
The certification authority is chosen according to several criteria. If the certification authority is well known, the certificate will be authorized by many browsers, however the price to pay will be expensive.
To get a digital certificate:
- Generate a private key using the
GENERATE ENCRYPTION KEYPAIRcommand.
For security reasons, the private key should always be kept secret. Actually, it should always remain with the server machine. For the Web server, the Key.pem file must be placed in the Project folder.
Use the
GENERATE CERTIFICATE REQUESTcommand to issue a certificate request.Send the certificate request to the chosen certificate authority. To fill in a certificate request, you might need to contact the certification authority. The certification authority checks that the information transmitted are correct. The certificate request is generated in a BLOB using the PKCS format encoded in base64 (PEM format). This principle allows you to copy and paste the keys as text and to send them via E-mail without modifying the key content. For example, you can save the BLOB containing the certificate request in a text document (using the
BLOB TO DOCUMENTcommand), then open and copy and paste its content in a mail or a Web form to be sent to the certification authority.Once you get your certificate, create a text file named “cert.pem” and paste the contents of the certificate into it. You can receive a certificate in different ways (usually by email or HTML form). 4D accepts all platform-related text formats for certificates (OS X, PC, Linux, etc.). However, the certificate must be in PEM format, i.e., PKCS encoded in base64.
CR line-ending characters are not supported on their own; you must use CRLF or LF.
Place the “cert.pem” file in the appropriate location.
The 4D server can now work in a secured mode. A certificate is valid between 3 months to a year.
Installation and activation
key.pem and cert.pem files
To be able to use the TLS protocol with the server, you must install the key.pem (document containing the private encryption key) and cert.pem (document containing the certificate) at the appropriate location:
- with 4D in local mode or 4D Server, these files must be placed next to the project folder
- with 4D in remote mode, these files must be located in the client database folder on the remote machine (for more information about the location of this folder, see the
Get 4D foldercommand).
You must copy these files manually on the remote machine.
Default key.pem and cert.pem files are provided with 4D. For a higher level of security, we strongly recommend that you replace these files with your own certificates.
Enabling TLS
The installation of key.pem and cert.pem files makes it possible to use TLS with the 4D server. However, in order for TLS connections to be accepted by the server, you must enable them:
- With the 4D web server, you must enable HTTPS. You can set the HSTS option to redirect browsers trying to connect in http mode.
- With the application server, you must select the Encrypt Client-Server Communications option in the "Client-server/Network options" page of the Settings dialog box.
- With the SQL server, you must select the Enable TLS option in the "SQL" page of the Settings dialog box.
The 4D web server also supports HSTS option to prevent a browser from
Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS)
PFS adds an additional layer of security to your communications. Rather than using pre-established exchange keys, PFS creates session keys cooperatively between the communicating parties using Diffie-Hellman (DH) algorithms. The joint manner in which the keys are constructed creates a "shared secret" which impedes outside parties from being able to compromise them.
When TLS is enabled on the server, PFS is automatically enabled. If the dhparams.pem file (document containing the server's DH private key) does not already exist, 4D will automatically generate it with a key size of 2048. The initial generation of this file could take several minutes. The file is placed with the key.pem and cert.pem files.
If you use a custom cipher list and want to enable PFS, you must verify that it contains entries with DH or ECDH (Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman) algorithms.